Did you know that approximately 600,000 women undergo tubal ligation (female sterilization) in the United States annually? Tubal Ligation, often referred to as ‘getting your tubes tied,’ has become a pivotal discussion in women’s healthcare and family planning. In this ultimate guide, we’ll unveil every layer of this procedure, from its historical roots to the modern-day practices, ensuring you have all the information you need to navigate this significant decision. Let’s dive in!
Key Takeaways:
- Tubal ligation is a permanent form of birth control that involves blocking or sealing the fallopian tubes to prevent eggs from reaching the uterus for fertilization.
- The procedure is highly effective, permanent, hormone-free, and cost-effective.
- Risks associated with tubal ligation include pain and discomfort, infection, bleeding, and failure.
- The procedure can be done using a variety of techniques, including laparoscopy, mini-laparotomy, and hysteroscopy.
- Tubal ligation is not reversible in all cases, and the success rate of reversal varies.
- Women will still have periods after tubal ligation.
Relevant Statistics and Facts
- According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), tubal ligation is the second most common form of contraception among women aged 15-44 in the United States.
- The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) reports that tubal ligation is more than 99% effective at preventing pregnancy.
- The procedure is typically performed as an outpatient surgery and can be done using a variety of techniques, including laparoscopy, mini-laparotomy, and hysteroscopy.
More about Tubal Ligation as a Procedure
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Procedure Type | Surgical |
| Duration | Approximately 30 minutes |
| Recovery Time | Varies (few days to weeks) |
| Effectiveness | Over 99% |
| Reversibility | Possible but with varying success rates |
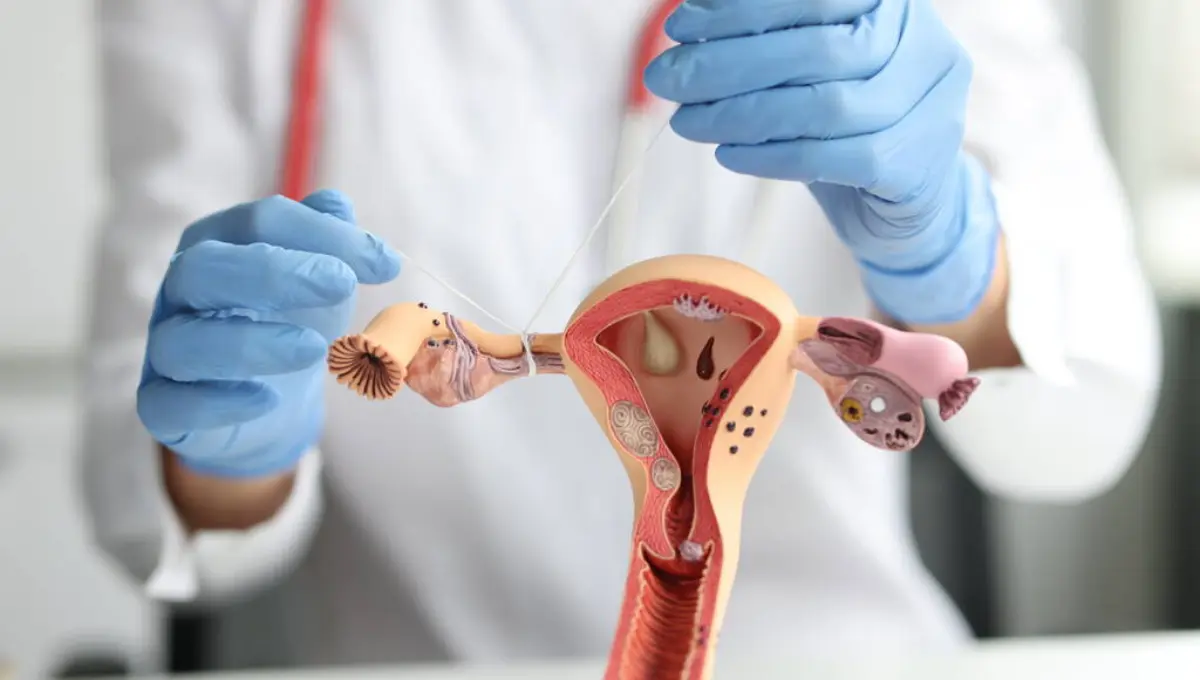
What is Tubal Ligation (Tubes Tied)?
Tubal Ligation is a surgical procedure aimed at providing permanent contraception for women. It involves the sealing, tying, or otherwise obstructing the fallopian tubes, thereby preventing eggs from reaching the uterus and subsequently, thwarting fertilization.
The surgery, predominantly performed through a minimally invasive method known as laparoscopy, involves making small incisions near the navel, through which instruments are inserted to access and obstruct the fallopian tubes.
What are the Benefits of Tubal Ligation?
Tubal ligation offers several benefits for women who are looking for a permanent form of birth control. Some of the most significant benefits include:
- Highly effective: Tubal ligation is more than 99% effective at preventing pregnancy, making it one of the most reliable forms of birth control available.
- Permanent: Unlike other forms of birth control, such as the pill or IUD, tubal ligation is a permanent procedure that does not require ongoing maintenance or monitoring.
- Hormone-free: Tubal ligation does not involve the use of hormones, which can be a significant advantage for women who experience side effects from hormonal birth control.
- Cost-effective: While the upfront cost of tubal ligation may be higher than other forms of birth control, it can be more cost-effective in the long run since it does not require ongoing expenses for contraception.
What are the Risks of Tubal Ligation?
While tubal ligation is generally considered safe, like any surgical procedure, it does carry some risks. Some of the most common risks associated with tubal ligation include:
- Pain and discomfort: After the procedure, women may experience pain and discomfort in the abdomen, which can last for several days.
- Infection: As with any surgical procedure, there is a risk of infection at the site of the incision.
- Bleeding: Women may experience some bleeding after the procedure, which is typically mild and resolves on its own.
- Failure: While tubal ligation is highly effective, there is still a small risk of failure, which can result in an unintended pregnancy.
What are the Common Techniques of Tubal Ligation?
Tubal ligation is typically performed as an outpatient surgery and can be done using a variety of techniques. Some of the most common techniques include:
- Laparoscopy: This involves making small incisions in the abdomen and using a laparoscope to view the fallopian tubes and block or seal them.
- Mini-laparotomy: This involves making a small incision in the abdomen and using a special instrument to block or seal the fallopian tubes.
- Hysteroscopy: This involves inserting a small camera through the cervix and into the uterus to view the fallopian tubes and block or seal them.
The specific technique used will depend on a variety of factors, including the woman’s age, medical history, and personal preferences.
How is the Life After the Procedure?
Recovery and Beyond
Post-procedure, individuals may experience some discomfort, which typically subsides within a few days. It’s crucial to follow all post-operative care instructions and to consult with your healthcare provider regarding any concerns or symptoms.
Emotional and Physical Changes
Understanding and navigating through the emotional and physical changes post-procedure is vital. While tubal ligation does not directly impact hormonal levels or sexual drive, the permanence of the decision may have emotional implications for some.
Where does the Egg go after Tubal Ligation?
After tubal ligation, the eggs are still released from the ovaries during ovulation, but they are absorbed by the body since they cannot travel down the blocked fallopian tubes to reach the uterus.
How Long after Tubes Tied can Tubes Grow Back?
It’s rare, but it is possible for the fallopian tubes to reconnect naturally over time, a phenomenon known as recanalization. This can happen months or years after the procedure, but the exact timeframe and likelihood are not definitively established.
How does Menstruation Occur after Tubes Tied?
Menstruation should occur as normal after tubes tied because the procedure does not affect the ovaries, where eggs are produced, or the menstrual cycle. The eggs are still released and broken down, but they do not reach the uterus due to the blocked tubes.
How Much does a Tubal Ligation Cost?
The cost of tubal ligation can vary widely based on location, healthcare provider, and insurance coverage. In the United States, without insurance, the cost can range from $1,500 to $6,000 or more. It’s essential to consult with healthcare providers and insurance for accurate pricing.
How to Get Pregnant after Tubes Tied?
Pregnancy after tubal ligation typically requires medical intervention. In-vitro fertilization (IVF) is a common method used to help women conceive after having their tubes tied. Another option could be tubal ligation reversal, a procedure to reconnect the fallopian tubes, but it’s not always possible and does not guarantee fertility restoration.
Sex after Tubal Ligation: How Soon?
The timeframe for resuming sexual activity after tubal ligation can depend on the individual and the specific method of ligation used. Generally, healthcare providers might recommend waiting for a specific period, often a few days to weeks, to allow for recovery and healing. Always follow the advice of your healthcare provider.
Tubal ligation vs. Vasectomy?
Both tubal ligation and vasectomy are permanent forms of sterilization for women and men, respectively. Tubal ligation involves blocking the fallopian tubes to prevent eggs from reaching the uterus, while a vasectomy involves cutting or blocking the vas deferens to prevent sperm from being released during ejaculation. Vasectomy is generally considered less invasive and has fewer risks and a shorter recovery time compared to tubal ligation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How long does the procedure take?
The procedure typically takes between 30 minutes and 1 hour to complete, depending on the technique used.
Is tubal ligation reversible?
While tubal ligation is considered a permanent form of birth control, it is possible to reverse the procedure in some cases. However, the success rate of tubal ligation reversal varies and is generally lower than the success rate of the initial procedure.
Will I still have periods after tubal ligation?
Yes, tubal ligation does not affect a woman’s menstrual cycle or hormone levels.
Conclusion
In wrapping up our comprehensive guide, Tubal Ligation stands out as a significant procedure in the realm of family planning and women’s healthcare. Whether you’re considering this procedure or seeking to understand it better, having a well-rounded perspective, from its historical context to modern-day practices, is imperative. Always consult with healthcare professionals, weigh the pros and cons, and ensure that your decision is well-informed and aligned with your future plans.












