Pregnancy is a time when the whole body is under tremendous pressure and a lot of changes are going on in the body. The three trimesters see a woman undergo a lot of symptoms, pelvic pain (groin pain) during pregnancy, is also one such symptom and is a very common occurrence.
Related: When Do Pregnancy Cravings Start?
Key Takeaways
Before we delve into the various causes and remedies for pelvic pain during pregnancy, here are some key takeaways:
- Pelvic pain during pregnancy is a common occurrence.
- It can result from various factors, including hormonal changes and physical strain.
- Relief options include lifestyle adjustments, exercises, and medical interventions.
- Consult with your healthcare provider for personalized guidance on managing pelvic pain during pregnancy.
What is Pelvic Pain During Pregnancy?
Pelvic pain (groin pain) is discomfort or pain that is felt in the lower abdomen, the area below the belly button and above the legs. It can be a sharp or dull ache and can be constant or intermittent. The pain can be caused by a variety of conditions such as ovarian cysts, endometriosis, pelvic inflammatory disease, or even pregnancy. Other causes of pelvic pain can be related to the urinary or gastrointestinal system, or even conditions such as fibromyalgia or irritable bowel syndrome.
Data and Stats related to Pelvic Pain During Pregnancy
Pelvic pain is a common issue during pregnancy, affecting approximately 50% of women. Here are some data and stats related to pelvic pain during pregnancy:
- The average reported prevalence of pregnancy-related pelvic girdle pain is 45.3% (range, 3.9-89.9%) in 28 studies.
- The overall prevalence of pelvic girdle pain among pregnant women was 24.3% with 95% CI (20.3-28.8).
- The prevalence of PGP and/or LBP during pregnancy is estimated to be 50% (3.9%-89.9%).
- 20% of pregnant women experience PGP that is severe enough to need medical help.
- Lower back pain and pelvic girdle pain (PGP) are common conditions in pregnancy, with an estimated incidence of 4-84%.
- Pain is not limited to a particular trimester during pregnancy but is often experienced throughout pregnancy and postpartum; however, the onset is usually at 14-30 weeks gestation.
- 25% of the women who experience pelvic girdle pain report having severe pain and 8% report pain that is disabling.
It is important to seek medical help if you experience pelvic pain during pregnancy, especially if it is severe or lasts for a long time.
How to differentiate between Pelvic Pressure and Pain?
Differentiating between pelvic pressure and pain can be challenging, as they can have similar underlying causes and overlapping symptoms. However, there are some key differences that can help you understand and describe your symptoms:
- Pelvic pressure: Pelvic pressure is often described as a sensation of heaviness, fullness, or discomfort in the lower abdomen, pelvis, or groin area. It can be a normal part of pregnancy, as the growing uterus puts pressure on the surrounding organs and tissues. In some cases, pelvic pressure may be a sign of cervical effacement and impending labor.
- Pelvic pain: Pelvic pain (groin pain) is typically described as a dull ache, sharp pain, or cramping sensation in the lower abdomen, pelvis, or groin area. It can be constant or intermittent and may be accompanied by other symptoms such as bloating, swelling, or changes in bowel or bladder function. Pelvic pain can have various causes, including muscle spasms, infections, reproductive system issues, digestive system issues, or other underlying conditions.
To help your healthcare provider better understand your symptoms, try to:
- Describe the location: Pelvic pressure is often felt in the lower abdomen, while pelvic pain can be more localized or spread across the entire pelvic area.
- Explain the sensation: Pelvic pressure is often described as a feeling of fullness or heaviness, while pelvic pain can be sharp, dull, or cramp-like.
- Note any accompanying symptoms: Pay attention to any additional symptoms you may be experiencing, such as changes in bowel or bladder function, vaginal bleeding, or abnormal discharge, as these can help your healthcare provider determine the underlying cause of your symptoms.
What are the Common Locations for Pelvic Pain During pregnancy?
The common locations for pelvic pain during pregnancy include:
- Lower back: Pelvic girdle pain (PGP) refers to pain or discomfort in the lower back or pelvis during pregnancy. PGP is a collection of uncomfortable symptoms caused by a stiffness of your pelvic joints or the joints moving unevenly at either the back or front of your pelvis.
- Pelvis: Pelvic pain can be felt deep in the pubic area, lower back, hips, groin, thighs, or knees.
- Hips and thighs: Pelvic girdle pain refers to pain or discomfort in your lower back, pelvis, hips, or thighs during pregnancy.
- Perineum: Pelvic pain can also be felt in the area between your vagina and anus (perineum).
What Causes Pelvic Pain During Pregnancy
There are many different causes of this pain, most are non serious, but sometimes this pain can signify something more serious.
Round Ligament Pain
Round ligament pain is a common type of pelvic floor pain during pregnancy. It is caused by the stretching of the round ligaments, which are the muscles that support the uterus as it expands to accommodate the growing fetus. The pain is usually felt on one or both sides of the lower abdomen, and can be sharp and sudden, or dull and achy.
Round ligament pain typically occurs during the second trimester, as the uterus begins to grow rapidly and the ligaments stretch to support it. However, it can also occur earlier or later in the pregnancy. The pain may be triggered by sudden movements, such as getting out of bed, rolling over in bed, or sneezing, and it may also be triggered by physical activity.
There are several things that can be done to alleviate round ligament pain:
- Rest: Try to get plenty of rest and avoid standing or sitting for long periods of time.
- Heat: Applying heat to the pelvic area can help to relax the muscles and relieve pain. You can use a heating pad, a hot water bottle, or a warm bath.
- Gentle exercise: Low-impact exercises such as walking, swimming, or prenatal yoga can help to strengthen the muscles in the pelvic area and relieve pain.
- Prenatal chiropractic care: Chiropractic care can help to realign the pelvic bones, relieve pain, and improve mobility.
- Avoid sudden movements: Try to be mindful of your movements and avoid sudden twisting or bending motions.
- Proper support: Use a pregnancy pillow to support your stomach and legs while you sleep.
Related: Why I Am Experiencing Belly Button Pain Or Itching Or Soreness?
Symphysis Pubis Dysfunction
Symphysis pubis dysfunction (SPD) is a condition that causes pain in the pelvic area during pregnancy. It is caused by a misalignment or excessive movement of the symphysis pubis, which is the joint located at the front of the pelvis. Symptoms of SPD include pain in the pelvic area, especially when standing on one leg, walking, or climbing stairs. The pain may also radiate to the thighs or lower back.
Treatment for SPD typically includes physical therapy, exercises to strengthen the muscles around the pelvic area, and pain management techniques such as ice or heat therapy and over-the-counter pain medication. Women with SPD may also need to use a pelvic support belt to help alleviate the pain. It is important to consult with obstetrician or a physiotherapist for proper diagnosis and management.
Related: How Can I Tell If I Am Pregnant With Twins?
Diastasis Recti
Diastasis recti is a condition that occurs during pregnancy where the abdominal muscles separate, resulting in a gap or “divarication” between the two sides of the rectus abdominis muscles. This separation can cause a bulging of the abdominal wall and can lead to abdominal weakness and instability.
It can also cause lower back pain and pelvic pain during pregnancy, as well as postpartum.
Physical therapy and exercises that focus on strengthening the abdominal muscles and improving core stability can help alleviate the symptoms associated with diastasis recti. It is important to consult with obstetrician or a physiotherapist for proper diagnosis and management.
It is important to note that not all abdominal separation will cause pain or discomfort, and not all abdominal separation will require treatment.
Related: Vaginal Discharge During Pregnancy
Braxton Hicks Contractions
Braxton Hicks contractions are irregular, usually painless contractions that occur during pregnancy. They are also known as “false labor” because they may feel similar to true labor contractions, but they do not result in the opening of the cervix or the birth of the baby. They are thought to be the uterus’s way of preparing for labor.
Braxton Hicks contractions can occur at any time during pregnancy, but they are most common during the second trimester and the third trimester. They may feel like a tightening or squeezing sensation in the pelvis, and can last for several seconds to a few minutes. They are usually not painful, but can be uncomfortable. They can be caused by dehydration, so drink plenty of water. Call your physician if you experience more than four contractions per hour for two hours straight; you may be in labor.
There are several things that can be done to alleviate Braxton Hicks contractions:
- Change positions: Try to change positions, such as by walking or sitting down.
- Relax: Try to relax, such as by taking a warm bath or reading a book.
- Hydrate: Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated, as dehydration can cause contractions.
- Avoid triggers: Avoid triggers such as smoking, caffeine or stress, which can cause contractions.
- Consult with your doctor: If the contractions are frequent or painful, or if you have any other concerns, please consult with your healthcare provider.
Related: Can I Have Sex While Pregnant?
Urinary Tract Infections
A urinary tract infection (UTI) during pregnancy can cause pelvic pain, as well as other symptoms such as frequent urination, a burning sensation when urinating, and cloudy, dark, bloody, or foul-smelling urine. UTIs are caused by bacteria that infect the urinary tract, and they are more common during pregnancy due to hormonal changes that can cause the urinary tract to become more susceptible to infection. It’s important to note that untreated UTIs during pregnancy can lead to serious complications such as preterm labor, so it’s important to address them promptly.
To prevent UTIs during pregnancy, it’s important to:
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water to flush out bacteria from the urinary tract.
- Empty your bladder regularly: Urinate as soon as you feel the urge, and try to empty your bladder completely each time.
- Wipe from front to back: Wipe from front to back after using the toilet to prevent bacteria from the anal area from spreading to the urinary tract.
- Avoid irritating feminine products: Avoid using perfumed soaps, powders, or other feminine products that can irritate the urinary tract.
- Wear breathable underwear: Wear cotton underwear and avoid tight pants, as they can trap moisture and bacteria.
Related: What Does Antenatal Classes Mean?
Gastrointestinal Issues
Gastrointestinal issues such as constipation, gas, and heartburn can cause pelvic pain during pregnancy. These issues are common during pregnancy due to hormonal changes that can slow down the digestive process and relax the muscles of the gastrointestinal tract.
To alleviate pelvic pain caused by gastrointestinal issues during pregnancy, it’s important to:
- Eat a healthy diet: Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains in your diet, and avoid foods that are high in fat, sugar, or spice.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water to help prevent constipation and keep the stool soft.
- Exercise: Regular exercise can help to relieve constipation and gas.
- Avoid lying down after eating: Wait at least 2-3 hours before lying down after eating to prevent acid reflux.
- Over-the-counter medication: Your healthcare provider may recommend antacids, or other medication that is safe to use during pregnancy to relieve heartburn.
- Fiber supplement: Your healthcare provider may recommend a fiber supplement to relieve constipation.
Related: Create Your Birth Plan – Checklist for Parents
Miscarriage
Miscarriage is the loss of a pregnancy before the 20th week and it can cause pelvic pain during early pregnancy. Miscarriage is a common complication of pregnancy, occurring in about 10-25% of known pregnancies. In addition to pelvic pain, other symptoms of a miscarriage may include vaginal bleeding or spotting, cramping, and the passing of tissue or clots.
If you experience pelvic pain during early pregnancy, it is important to seek medical attention immediately, as it could be a sign of a miscarriage. Your healthcare provider will be able to perform an examination and possibly a ultrasound to confirm if the pregnancy is viable or not. They may also do blood test to check for the level of pregnancy hormones like hCG.
If a miscarriage is confirmed, there are different ways it can be treated, such as:
- Watchful Waiting: This is when the bleeding and cramping stop on their own and the tissue is passed naturally.
- Medication: Medications can be given to help the tissue pass and to control the bleeding.
- Dilation and curettage (D&C): This is a procedure in which the cervix is dilated and the tissue is removed from the uterus.
It’s important to note that experiencing pelvic pain during early pregnancy does not always mean a miscarriage is happening, other conditions such as an ectopic pregnancy or a threatened miscarriage could have similar symptoms. Your healthcare provider will be able to determine the cause of the pain and provide the appropriate care and treatment.
Losing a pregnancy can be a difficult and emotional time, so it’s important to take time to grieve and to seek.
Related: What Are The Different Types Of Breast Pump?
Ectopic Pregnancy
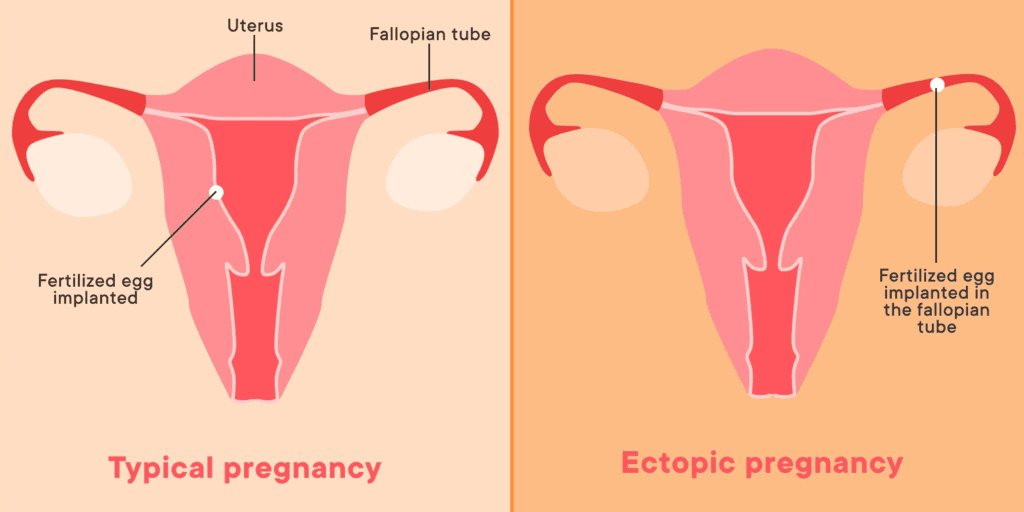
Ectopic pregnancy is a serious condition in which a fertilized egg implants outside of the uterus, usually in the fallopian tubes. This can cause severe pelvic pain, as well as other symptoms such as vaginal bleeding, nausea, and lightheadedness. If left untreated, an ectopic pregnancy can rupture and cause life-threatening internal bleeding. If you suspect you may have an ectopic pregnancy, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. Treatment typically involves medication or surgery to remove the ectopic tissue.
Related: What Is A Molar Pregnancy?
Uterine Rupture
Uterine rupture is a rare but serious complication of pregnancy, in which the uterus tears along the site of a previous cesarean section or other uterine surgery. It can cause severe abdominal pain and bleeding, and can be life-threatening for both the mother and the baby. Symptoms of uterine rupture may include severe abdominal pain, tenderness, back pain, and a sudden decrease in fetal movement.
Uterine rupture is considered a medical emergency and requires immediate treatment, which typically involves an emergency cesarean section to deliver the baby as soon as possible. In some cases, a hysterectomy (removal of the uterus) may be necessary to control bleeding.
Placental Abruption
Placental abruption is a serious condition that occurs when the placenta separates from the inner wall of the uterus before delivery. This can cause severe abdominal and pelvic pain, along with vaginal bleeding. If you suspect that you may have placental abruption, it’s important to seek immediate medical attention as it can be life-threatening for both the mother and the baby.
Symptoms of placental abruption include:
- Severe abdominal or pelvic pain
- Vaginal bleeding
- Abdominal tenderness
- Uterine contractions
- Rapid heartbeat
- Back pain
- Decrease in fetal movement
Treatment for placental abruption typically involves close monitoring of both the mother and the baby. In some cases, the baby may need to be delivered early to ensure the safety of both mother and baby.
It is important to note that placental abruption is a serious condition and requires prompt medical attention.
Related: 10 Comfortable Pregnancy Sex Positions
Uterine Fibroids
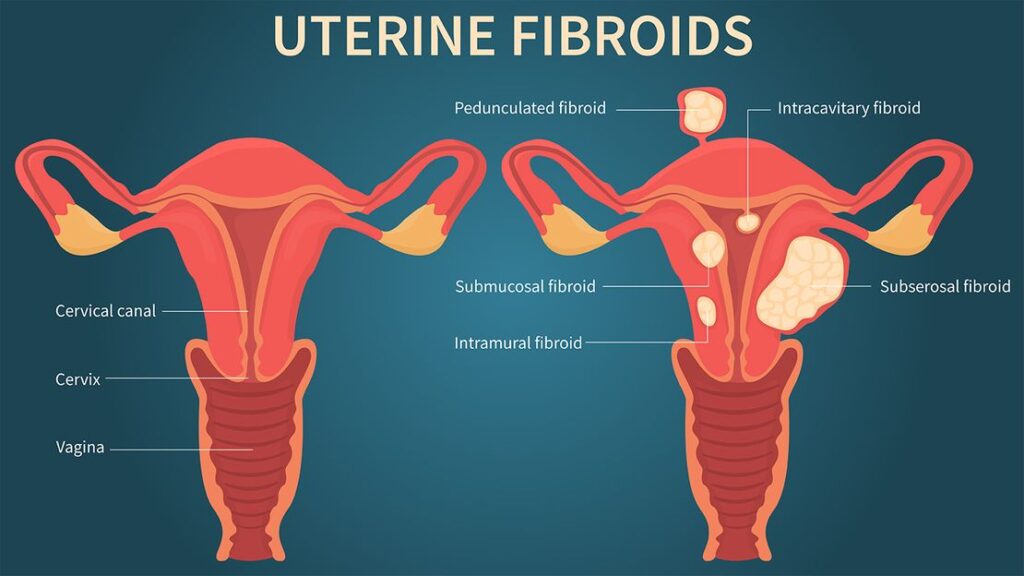
Uterine fibroids are non-cancerous growths that develop in the uterus and can cause pain in the pelvis during pregnancy. These growths are caused by an overgrowth of the muscle cells of the uterus and can vary in size from small to large. They can also be located in different areas of the uterus such as submucosal, intramural, or subserosal.
Symptoms of uterine fibroids during pregnancy may include:
- Pelvic pain or pressure
- Abdominal swelling or bloating
- Constipation
- Frequent urination
- Heavy or prolonged menstrual periods
- Pain during intercourse
- Lower back pain
While fibroids are common, not all women with fibroids experience symptoms. Also, the symptoms may vary depending on the size, location, and number of fibroids.
Treatment for uterine fibroids during pregnancy typically depends on the size and location of the fibroid, as well as the stage of pregnancy. In most cases, fibroids will be monitored throughout the pregnancy to ensure that they are not causing problems for the mother or the baby. In some cases, surgery may be necessary after the baby is delivered.
Related: Should I Have the Flu Vaccine During Pregnancy?
Preeclampsia
Preeclampsia is a condition that can occur during pregnancy characterized by high blood pressure and damage to organs such as the liver and kidneys. Some women may experience pelvic pain as a symptom of preeclampsia. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider as soon as possible if you experience any symptoms of preeclampsia, as it can be a serious condition that can lead to complications for both the mother and the baby if left untreated.
Vulvodynia
Vulvodynia is a chronic pain condition that affects the vulva and can cause pelvic pain during pregnancy.
Treatment options for vulvodynia during pregnancy may include physical therapy, medications, and lifestyle changes. It is important to work with a healthcare provider to create a treatment plan that is safe for both mother and baby. It may also involve avoiding certain triggers or activities that worsen pain and learning techniques for managing pain. In addition, it is important to address any emotional or psychological factors that may be contributing to the pain.
Ovarian Torsion
Ovarian torsion is a medical emergency that occurs when an ovary twists on itself, cutting off its own blood supply. This can cause severe pelvic pain during pregnancy. Other symptoms may include nausea, vomiting, and fever.
Ovarian torsion is a rare condition, but it is important to seek immediate medical attention if you suspect you may have it as it can cause damage to the ovary and fallopian tube if not treated promptly. The usual treatment for ovarian torsion is surgery to untwist the ovary and preserve as much of the ovary as possible. In some cases, the ovary may need to be removed.
Preterm Labor
Preterm labor is labor that occurs before 37 weeks of pregnancy. Pelvic pain is a common symptom of preterm labor, along with contractions, cramping, and a feeling of pressure in the pelvic area. Other symptoms may include back pain, diarrhea, and a change in vaginal discharge.
If you suspect you are experiencing preterm labor, it’s important to contact your healthcare provider immediately. They may administer a pelvic exam, ultrasound or other diagnostic tests to determine if you are in labor. If you are in preterm labor, your healthcare provider may try to stop labor and give you medications to mature your baby’s lungs. In some cases, delivery may be necessary to prevent further complications.
Related: What are Best 10 Prenatal Vitamins for a Healthy Pregnancy?
Appendicitis
Appendicitis is a condition, in which the appendix becomes inflamed and infected. It can cause severe abdominal pain, particularly in the lower right side of the abdomen. Other symptoms may include nausea, vomiting, and fever. Appendicitis during pregnancy can be particularly challenging to diagnose because the symptoms can be similar to those of a normal pregnancy.
The usual treatment for appendicitis is surgery to remove the infected appendix, called an appendectomy. In pregnancy, it is generally performed during the second trimester, when the risk to the developing fetus is lowest.
How to Relieve Pelvic Pain During Pregnancy?
There are several things that can help relieve pelvic pain during pregnancy:
- Rest: Try to get plenty of rest and avoid standing or sitting for long periods of time.
- Exercise: Low-impact exercises such as walking, swimming, or prenatal yoga can help to strengthen the muscles in the pelvic area and relieve pain.
- Heat: Applying heat to the pelvic area can help to relax the muscles and relieve pain. You can use a heating pad, a hot water bottle, or a warm bath.
- Stretching: Gentle stretching exercises can help to relieve pain and tension in the pelvic area.
- Chiropractic care: Chiropractic care can help to realign the pelvic bones, relieve pain and improve mobility.
- Acupuncture: Some studies have shown that acupuncture can be effective in reducing pelvic pain during pregnancy.
- Prenatal massage: Prenatal massage can help to relieve tension and pain in the pelvic area.
- Over-the-counter pain medication: Acetaminophen (Tylenol) is considered safe to use during pregnancy, but always check with your healthcare provider before taking any medication.
It’s important to note that not all of these methods may be appropriate for everyone, and it’s important to consult with your healthcare provider to determine what will work best for you.
Related: Aches and Pains During Pregnancy
How to Sleep with Pelvic Pain During Pregnancy?
- Sleep on your side: Sleeping on your side, specifically on your left side, can help take pressure off your back and pelvis.
- Use a pregnancy pillow: A pregnancy pillow can help support your belly and legs, taking pressure off your pelvis.
- Use a maternity support belt: Maternity support belt can help with the back and abdomen and can lift some pain up off the pelvis
- Avoid sleeping on your back: Sleeping on your back can cause your belly to sag and put pressure on your lower back and pelvis.
- Use a heating pad: Placing a heating pad on your lower back or pelvis can help relax the muscles and alleviate pain.
- Practice good posture: Good posture can help align your spine and take pressure off your pelvis.
- Talk to your doctor: Consult with your healthcare provider if your pelvic pain is severe or persistent, they may recommend physical therapy or other treatments.
Related: What Are Common Discomforts During Pregnancy?
When to Call a Doctor For Pelvic Pain During Pregnancy?
You should call your doctor immediately if you experience any of the following:
- Severe or sharp pain in the pelvic area causing difficulty walking or standing
- Pain that radiates to the shoulder or neck
- Severe headache
- Persistent nausea or vomiting
- Fever or chills
- Dizziness or fainting
- Abdominal swelling
- Watery, greenish, or bloody vaginal discharge or foul-smelling vaginal discharge
- Rapid or irregular contractions – more than 4 contractions an hour for 2 hours.
- Less than 10 fetal kick counts in 1 hour (between 28 weeks and delivery)
These symptoms could be an indication of a serious condition such as an ectopic pregnancy, preterm labor, or a miscarriage. It’s important to seek medical attention as soon as possible to ensure the health and safety of both you and your baby.
Even if you don’t have any of the above symptoms, if you have any concerns or questions about pelvic pain during pregnancy, please reach out to your doctor. They will be able to assess your condition and provide you with the appropriate care and treatment.
Related: What Are Common Discomforts During Pregnancy?
Conclusion
Now that you have a comprehensive understanding of the causes and relief options for pelvic pain during pregnancy, you can take proactive steps to ensure a more comfortable and enjoyable pregnancy journey. Remember to consult with your healthcare provider for personalized guidance and support throughout your pregnancy.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is pelvic pain during pregnancy normal?
Yes, pelvic pain during pregnancy is common and usually not a cause for concern. However, consult with your healthcare provider to rule out any serious issues.
When should I seek medical attention for pelvic pain during pregnancy?
If you experience severe or persistent pelvic pain, vaginal bleeding, or have concerns about your baby’s well-being, contact your healthcare provider immediately.
Can I take pain relievers for pelvic pain during pregnancy?
Some over-the-counter pain relievers may be safe, but always consult with your doctor before taking any medication during pregnancy.